
Introduction
RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) compliance is a critical aspect of printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) manufacturing, especially for companies aiming to meet environmental standards and legal requirements. As governments across the world continue to tighten regulations on hazardous substances, understanding RoHS compliance becomes essential for both manufacturers and consumers.
In this article, we will discuss the significance of RoHS in PCB assembly, explore how compliance affects the design and manufacturing process, and delve into testing, documentation, and future trends in RoHS-compliant PCBA.
What is RoHS Compliance in PCBA Assembly?
Understanding RoHS Regulations
RoHS, established by the European Union (EU), restricts the use of specific hazardous materials in electrical and electronic equipment (EEE). These materials include lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, and certain flame retardants, which pose significant environmental and health risks when released into the environment. The updated RoHS 3 directive, which came into effect in 2019, added new substances like phthalates to the restricted list, further tightening control over harmful chemicals.
The goal of RoHS compliance in PCB assembly is to ensure that electronic products, including PCBs, do not contain hazardous substances beyond allowed limits, thereby reducing environmental impact and protecting human health.
The Importance of RoHS Compliance for Electronics Manufacturers
RoHS compliance is not just a legal requirement for selling products in certain regions, such as the EU. It is also an essential factor in accessing global markets, including China, Japan, and California, where similar regulations exist. Non-compliance can result in product recalls, fines, and damage to a brand’s reputation.
For manufacturers, being RoHS-compliant means adhering to stringent regulations, which directly influence product design, materials selection, and manufacturing processes. Additionally, as consumer awareness of environmental issues increases, companies that comply with RoHS regulations may have a competitive advantage by demonstrating a commitment to sustainability.
Key Benefits of RoHS-Compliant PCBA
1. Environmental Responsibility: RoHS-compliant PCBs help minimize the environmental hazards posed by electronic waste, ensuring that harmful substances do not pollute landfills or water systems.
2. Consumer Safety: RoHS compliance protects consumers from potential health risks associated with toxic chemicals found in electronic devices. Products that meet RoHS standards are safer for both consumers and workers in the manufacturing process.
3. Market Access and Competitive Advantage: Adhering to RoHS regulations opens up access to international markets, especially in the EU, where RoHS compliance is mandatory. Additionally, many consumers prefer eco-friendly products, thus providing a potential competitive edge.
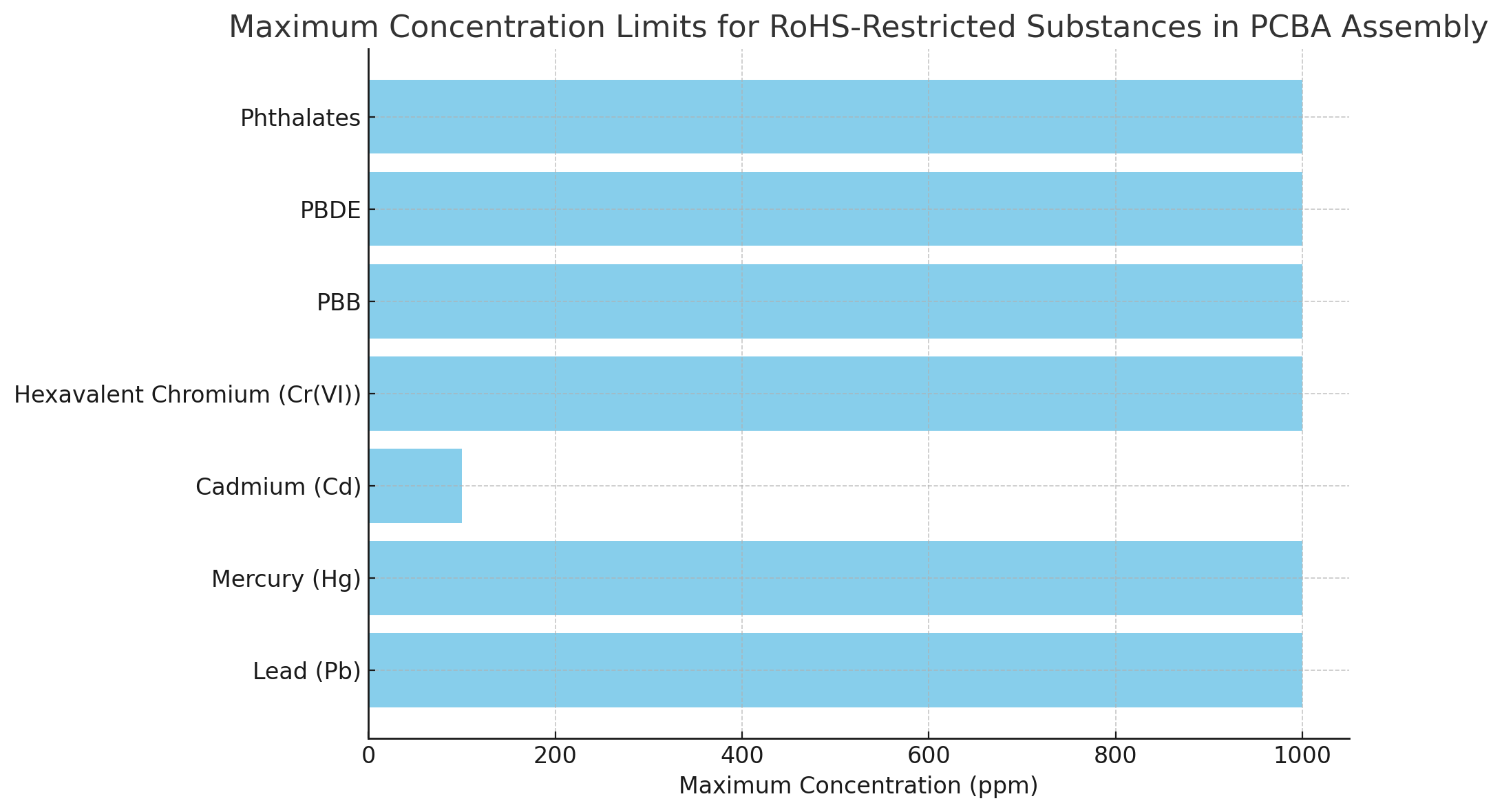
Substance | Maximum Limit | Impact on Health/Environment |
Lead (Pb) | < 1,000 ppm | Harmful to the nervous system |
Mercury (Hg) | < 1,000 ppm | Toxic to organs and the brain |
Cadmium (Cd) | < 100 ppm | Carcinogenic, affects kidneys |
Hexavalent Chromium (Cr(VI)) | < 1,000 ppm | Causes cancer and respiratory issues |
Polybrominated Biphenyls (PBB) | < 1,000 ppm | Environmental pollutant |
Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDE) | < 1,000 ppm | Endocrine disruptor, bioaccumulative |
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) | < 1,000 ppm | Reproductive toxicity |
Butyl Benzyl Phthalate (BBP) | < 1,000 ppm | Affects development and reproduction |
Dibutyl Phthalate (DBP) | < 1,000 ppm | Causes birth defects |
Diisobutyl Phthalate (DIBP) | < 1,000 ppm | Harmful to reproduction |
How RoHS Compliance Affects PCB Design and Assembly
Materials and Components Selection
RoHS compliance directly impacts the materials used in PCB assembly. Designers must choose materials that do not exceed the maximum allowable concentrations of restricted substances. For example, lead-free solder must be used instead of traditional lead-based solder, and eco-friendly laminates must replace those that contain harmful chemicals.
The selection of compliant materials can affect the entire production process, from component sourcing to the final assembly. Designers must collaborate closely with suppliers to ensure that all components used, including resistors, capacitors, and ICs, meet RoHS requirements.
The Role of Surface Finishes
Surface finishes are another key area influenced by RoHS compliance. Traditional lead-based finishes like HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling) have been replaced by lead-free alternatives. Common RoHS-compliant finishes include:
● ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold): Ideal for fine-pitch components, this finish provides good reliability and excellent solderability.
● OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative): A cost-effective and eco-friendly finish, OSP is used for simpler, lower-end applications.
● Immersion Silver and Tin: These finishes are often used in high-performance applications, offering good shelf life and high-quality solderability.
Each finish has its trade-offs, with differences in shelf life, solderability, and overall cost. Designers must choose the most suitable finish based on the project requirements, keeping in mind the limitations imposed by RoHS.
Surface Finish | Description | Pros | Cons |
ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold) | A high-quality surface finish, ideal for fine-pitch components. | Excellent for soldering, durable finish. | Expensive compared to other finishes. |
OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative) | Eco-friendly surface finish, using organic compounds. | Cost-effective, environmentally friendly. | Shorter shelf life, not ideal for all components. |
Immersion Silver | Provides a silver layer that prevents oxidation. | Good for fine-pitch components, affordable. | Sensitive to humidity, can tarnish over time. |
Lead-Free HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling) | A more affordable lead-free alternative to traditional HASL. | Cost-effective, commonly used. | Less smooth, lower quality than ENIG. |
Thermal Management and Process Adjustments
RoHS compliance introduces new challenges related to thermal management. Lead-free solders typically require higher reflow temperatures (240°C–260°C) compared to traditional lead-based solders. This can impact both the thermal resilience of the PCB materials and the assembly process.
PCB designers must adjust their designs to accommodate higher temperatures and ensure that the materials used are capable of withstanding these conditions. This may involve selecting substrates with higher glass transition temperatures (Tg) and ensuring that the solder joints are strong enough to endure the stresses of reflow soldering.
RoHS-Compliant Components and Supplier Management
Ensuring Component Compliance
Ensuring that all components used in the PCB assembly process are RoHS-compliant is a critical step in maintaining overall compliance. This involves sourcing components from suppliers who can guarantee that their products meet the restrictions outlined in RoHS regulations.
Manufacturers must request certificates of compliance (CoCs) from their suppliers to verify that the components meet RoHS standards. This documentation should be maintained throughout the production process to demonstrate traceability and compliance.
Challenges in Sourcing RoHS-Compliant Components
Sourcing RoHS-compliant components can be challenging, particularly for legacy components that were originally designed with lead-based materials. As technology advances and component manufacturers transition to RoHS-compliant parts, there may be supply chain issues or increased costs associated with sourcing alternatives.
Manufacturers must be proactive in identifying compliant components early in the design process to avoid delays. This may require collaboration with multiple suppliers and constant monitoring of component availability and cost.
Documentation and Certification
Proper documentation and certification are crucial for verifying RoHS compliance. Manufacturers should maintain detailed records of all materials and components used in the assembly process, including the certificates and declarations from suppliers.
Compliance documentation should be easily accessible for audits and regulatory inspections. This includes maintaining a compliance dossier with test results, supplier certificates, and material declarations to ensure transparency and accountability.
Manufacturing Process for RoHS-Compliant PCBAs
Adjusting Manufacturing Techniques for RoHS Compliance
The transition to RoHS-compliant PCB assembly requires manufacturers to adjust their fabrication techniques. These adjustments include the use of lead-free soldering, changes in surface finish applications, and ensuring that all components meet RoHS requirements.
Manufacturers must also update their equipment and processes to handle the challenges posed by RoHS-compliant materials. This may include implementing higher-temperature reflow soldering equipment and fine-tuning the PCB assembly process to ensure reliability and quality.
Impact of RoHS on Reflow Soldering
One of the most significant changes introduced by RoHS is the shift to lead-free soldering. Lead-free solders, while necessary for compliance, have higher melting points, which means the soldering process requires higher temperatures and may stress both the components and the PCB.
Manufacturers need to optimize reflow soldering profiles to achieve high-quality solder joints while avoiding damage to sensitive components. Careful monitoring and calibration of soldering equipment are crucial to maintain consistency and reliability in the final product.
Ensuring Reliability and Durability
RoHS-compliant PCBs must meet rigorous performance and durability standards, especially considering the impact of lead-free solder on the mechanical properties of solder joints. Lead-free solders can be more brittle than lead-based solders, which can affect the reliability of PCB assemblies.
To ensure durability, designers must consider the reliability of the materials used and conduct thorough testing, including thermal cycling, vibration testing, and mechanical stress testing, to verify that the final product meets quality standards.
Step | Description |
1. Material Selection | Choose lead-free, RoHS-compliant components and substrates. |
2. Soldering Process | Use lead-free solder alloys, such as SAC305 or SnCu. |
3. Surface Finishing | Apply RoHS-compliant surface finishes like ENIG or OSP. |
4. Component Sourcing | Ensure all components have RoHS certificates of compliance. |
5. Testing and Certification | Perform XRF analysis and obtain third-party lab reports to confirm compliance. |
Testing and Verifying RoHS Compliance in PCBAs
Common Testing Methods
To verify RoHS compliance, various testing methods can be used, including X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analysis and third-party laboratory testing. These methods help identify the presence of restricted substances in the components and materials used in PCB assembly.
Manufacturers should ensure that they partner with accredited laboratories for testing, as this helps confirm that the PCBs meet the strict RoHS standards. Regular testing is essential to maintain ongoing compliance and ensure that no hazardous substances exceed the allowable limits.
Importance of Compliance Documentation
Compliance documentation is vital for demonstrating adherence to RoHS regulations. Manufacturers should ensure that all necessary documentation, including CoCs, test reports, and supplier declarations, is collected and maintained.
This documentation is crucial for traceability, and it provides the necessary evidence to prove compliance during audits and regulatory inspections.
Future Trends in RoHS Compliance and PCBA Manufacturing
Expanding RoHS Regulations
As environmental concerns continue to grow, RoHS regulations are likely to evolve. For example, RoHS 3 introduced additional restrictions on phthalates, a class of chemicals used in plasticizers. Similar updates may occur in the future, with stricter regulations on additional substances.
Manufacturers should stay informed about the evolving regulatory landscape to ensure their products remain compliant. The trend towards stricter regulations is likely to continue as governments work to reduce the environmental impact of electronics manufacturing.
Innovations in Eco-Friendly Electronics
The shift to RoHS compliance is driving innovations in sustainable electronics. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices, such as reducing PCB size to minimize material waste, using recyclable components, and selecting environmentally friendly coatings and finishes.
This trend is expected to continue, with the electronics industry focusing on sustainability and reducing its carbon footprint. RoHS compliance will play a key role in this transition, pushing manufacturers to adopt greener practices and products.
Conclusion
RoHS compliance in PCB assembly is crucial for meeting environmental, health, and safety standards. It affects every step, from material selection to testing, ensuring product reliability and safety. By prioritizing RoHS, manufacturers can protect the environment and enhance their products' marketability. Partnering with a trusted RoHS-certified PCBA assembly provider, like XDCPCBA, helps ensure compliance, avoiding regulatory issues and supporting sustainability in the electronics industry.
FAQ
Q: What is RoHS-compliant PCBA assembly?
A: RoHS-compliant PCBA assembly ensures that all components and materials used in the process meet the Restriction of Hazardous Substances directive, reducing environmental and health risks.
Q: Why is RoHS compliance important for PCBA assembly?
A: RoHS compliance is crucial for meeting global environmental standards, ensuring that electronic products are safe for consumers and the environment.
Q: How does RoHS compliance affect PCBA assembly design?
A: RoHS compliance influences material selection, component sourcing, and manufacturing processes, requiring the use of lead-free solder and eco-friendly components.
Q: What components need to be RoHS compliant in PCBA assembly?
A: All components used in PCBA assembly, such as resistors, capacitors, and connectors, must be free of hazardous substances like lead and mercury to meet RoHS standards.
Q: How can I verify RoHS compliance in PCBA assembly?
A: RoHS compliance can be verified through supplier documentation, testing methods like XRF analysis, and certification reports from trusted manufacturers.













