
Introduction
PCBA assembly quality control ensures the final product meets design standards. Each assembly step must be checked to avoid defects and failures. In this article, we’ll explore the critical elements of PCBA assembly quality control and how to ensure high-quality results. You’ll learn what to check during the quality control process to ensure a reliable, functional product.
Initial Design Verification in PCBA Assembly Quality Control
Bill of Materials (BOM) Review
The Bill of Materials (BOM) is one of the first documents to review in the PCBA assembly process. Ensuring that all components listed in the BOM match the design specifications is crucial. Errors in the BOM can lead to incorrect parts being ordered, delayed production timelines, or even malfunctioning products. Double-checking manufacturer part numbers, tolerance levels, and verifying the compatibility of each component with the design ensures that only the correct and high-quality components are used.
Gerber File Validation
Gerber files are essential in guiding the PCB manufacturer on how to lay out the components on the board. These files provide detailed instructions on component placements, layer designs, and other critical features. Ensuring that Gerber files are accurate is a vital part of the quality control process. Errors in Gerber files can lead to incorrect component placements and soldering issues. It’s essential to cross-check component placements, pad sizes, and via alignments to ensure everything is correctly laid out for assembly.
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) Review
Before proceeding with the assembly, it's important to conduct a Design for Manufacturability (DFM) review. This step evaluates whether the PCB design is optimized for easy and efficient assembly. The goal is to minimize potential issues that could arise during manufacturing, such as trace width problems, hole size discrepancies, and thermal management issues. A thorough DFM review ensures that the design can be produced at scale with minimal issues, thereby reducing the risk of errors and delays during production.
Component Inspection
Component Sourcing and Compatibility
Not all components are equal, and sourcing components from reputable suppliers is key to ensuring the quality of the final PCBA. All components must meet quality and performance specifications, and the manufacturers should perform checks to verify that each part is genuine and appropriate for the design. Counterfeit or low-quality parts can lead to unreliable assemblies, which could cause product failures. It’s essential to ensure that the components used are of the highest quality and compatible with the design requirements.
Visual and Microscopic Inspection
Once components are sourced, they should be visually inspected, and for more detailed checks, microscopic inspection is necessary. This inspection ensures that all components are correctly placed, aligned, and oriented according to the design. It also helps in identifying any potential damage or missing components that could cause malfunctions later. Microscopic inspection is particularly important for smaller components, as it helps to spot issues that are not visible to the naked eye.
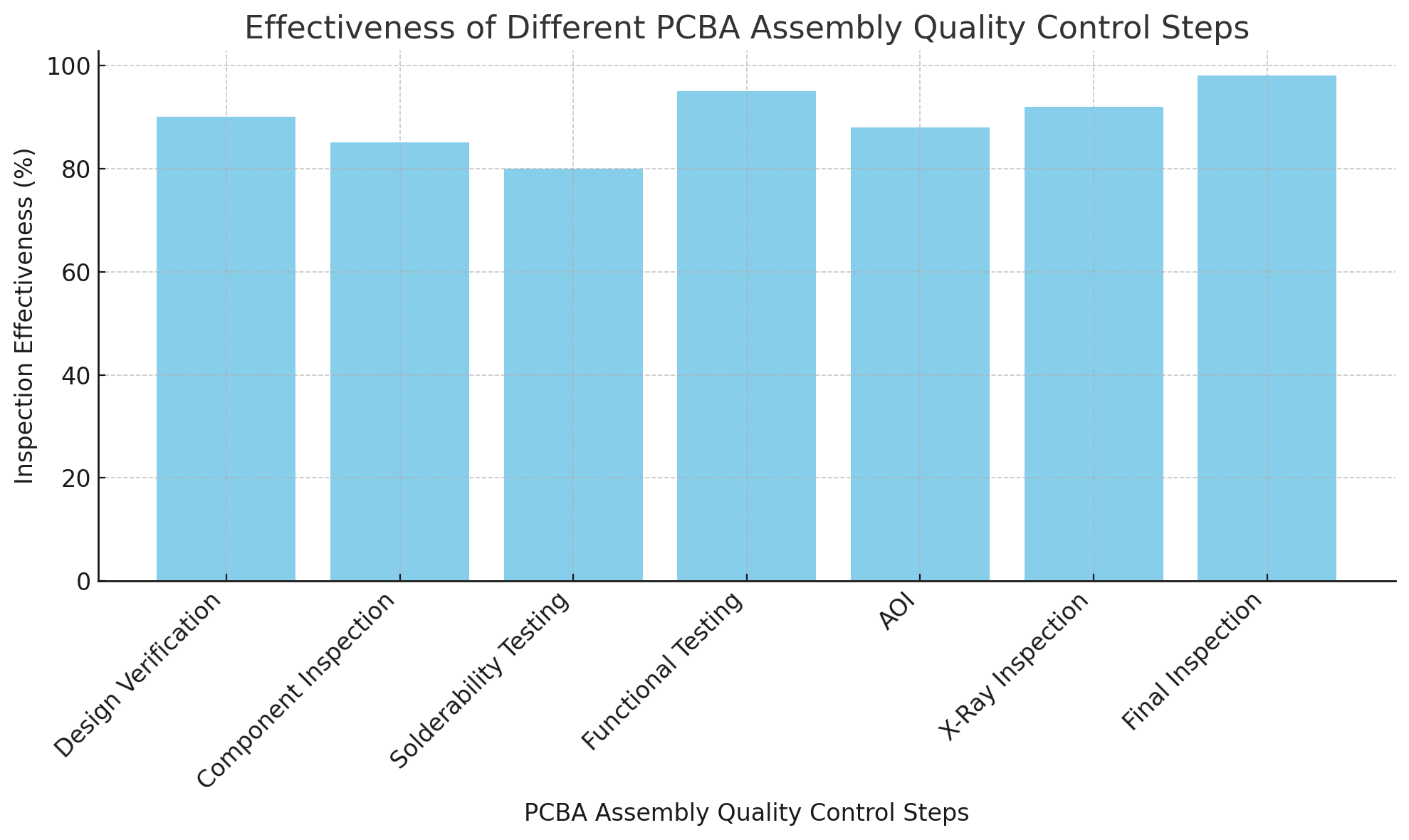
Solderability and Solder Joint Testing
Solderability Test
The solderability of components is critical for ensuring that electrical connections are made properly. Soldering issues such as cold joints, poor adhesion, or excessive solder can compromise the integrity of the PCB. A solderability test, such as the dip-and-look or wetting balance methods, is used to assess the quality of the solder joints. It’s essential to check the consistency of solder joints to ensure they provide secure and reliable electrical connections.
Solder Joint Inspection
After the soldering process, inspecting the solder joints is a crucial step in PCBA quality control. Solder joints should be checked for signs of cold joints, bridges, voids, or insufficient solder. Microscopic inspection tools can help detect any small defects that could affect the functionality of the PCB. Ensuring that all solder joints are well-formed and reliable is vital for the longevity and performance of the final product.
Testing Method | Purpose | Application |
Visual Inspection | Check for misaligned components or surface defects | Applied before and after assembly |
Solder Joint Inspection | Ensures solder joints are secure and without defects | Done during and post-soldering |
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) | Detects soldering issues like bridges and misplacements | Used both pre and post-soldering |
In-Circuit Testing (ICT) | Verifies electrical connections and component functionality | Checks for short circuits, open circuits, and component failures |
Functional Testing | Verifies that the PCBA works as intended | Performed under typical operational conditions |
X-Ray Inspection | Checks for hidden defects in multi-layer PCBs or BGA packages | Used for complex designs where optical methods can't detect internal issues |
Functional Testing
Electrical Testing
Electrical testing is a fundamental part of the PCBA assembly quality control process. In-circuit testing (ICT) helps verify the functionality of each component by checking for shorts, opens, resistance, and capacitance. This step ensures that each individual component on the PCB functions correctly before moving on to more extensive testing.
Full System Testing
While in-circuit testing focuses on individual components, full system testing ensures that the entire circuit functions as intended. During this stage, the assembled PCB is powered on, and all components are tested under operational conditions. Functional testing helps confirm that the PCBA meets design specifications and performs correctly in real-world applications.
Defect Type | Description | Detection Method |
Solder Bridges | Unintended connections between two or more pads | Visual Inspection, AOI |
Cold Solder Joints | Weak or poor-quality solder joints | Solder Joint Inspection, AOI |
Misplaced Components | Components not in their proper position | Visual Inspection, AOI |
Component Damage | Physical damage to components during assembly | Microscopic Inspection, AOI |
Open Circuits | Missing or broken electrical connections | In-Circuit Testing (ICT) |
Short Circuits | Unwanted electrical connections between traces | In-Circuit Testing (ICT), AOI |
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
Pre-Soldering AOI
Before soldering the components, a pre-soldering automated optical inspection (AOI) should be performed to check for correct component placement and alignment. AOI uses high-resolution cameras and algorithms to detect misaligned, missing, or incorrectly placed components. Early detection of such issues helps prevent costly errors later in the assembly process.
Post-Soldering AOI
After soldering, post-soldering AOI inspects the quality of the solder joints. This step detects issues such as insufficient solder, solder bridges, or component lifting. AOI systems use advanced image processing techniques to identify defects and ensure that the solder joints meet quality standards.
X-Ray Inspection for Hidden Defects
BGA and QFN Inspection
In complex designs, especially those with Ball Grid Array (BGA) or Quad Flat No-lead (QFN) packages, X-ray inspection is critical for detecting hidden defects. X-ray technology penetrates through the layers of the PCB and reveals issues that are not visible on the surface, such as solder voids, misaligned balls, or internal cracks.
Solder Joint Integrity
X-ray inspection is also used to verify the integrity of solder joints, especially in multi-layered PCBs or those with complex components. This inspection method ensures that the solder joints inside the components are reliable and conductive, preventing potential failures in the product’s operation.
Final Inspection and Approval
Visual and Functional Inspection
Once all previous tests have been completed, a final visual and functional inspection is conducted to ensure that the PCBA meets all specifications. Visual inspection looks for any surface defects, scratches, or misalignments, while functional testing confirms the board’s operational performance.
Quality Documentation and Certification
After the final inspection, it is essential to ensure that all quality control processes are documented and that the PCBA meets industry standards, such as IPC-A-610 and ISO 9001. Certification ensures that the assembly meets the required quality levels and provides traceability for future reference.
Standard | Description | Relevance |
IPC-A-610 | Acceptability of Electronic Assemblies | Provides criteria for judging the quality of soldering, components, and assembly |
ISO 9001 | Quality Management Systems | Ensures that the manufacturer follows consistent processes for quality control |
ISO 14001 | Environmental Management Systems | Ensures sustainable and environmentally friendly practices in PCB production |
RoHS Compliance | Restriction of Hazardous Substances | Guarantees that no harmful substances are present in the assembly, meeting environmental regulations |
Conclusion
PCBA assembly quality control is crucial for ensuring reliable, functional products. Through thorough checks, including design verification, component inspection, and functional testing, manufacturers can meet high-quality standards. A well-structured process minimizes defects and reduces costs, ensuring the product performs as expected. Partnering with experienced manufacturers like XDCPCBA ensures consistent quality and reliable results at every production stage.
FAQ
Q: What is PCBA assembly quality control?
A: PCBA assembly quality control ensures that the assembled circuit boards meet the required specifications for functionality, reliability, and performance.
Q: Why is component inspection important in PCBA assembly?
A: Component inspection ensures that all parts meet quality standards and are compatible with the design, preventing issues such as component misplacement or faulty parts.
Q: How is solderability tested in PCBA assembly?
A: Solderability is tested using methods like dip-and-look or wetting balance tests to ensure reliable electrical connections and durable solder joints.
Q: What is the role of Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) in PCBA assembly?
A: AOI helps detect defects such as misalignment, missing components, and soldering issues by using cameras and algorithms to inspect the boards during production.
Q: How does functional testing ensure quality in PCBA assembly?
A: Functional testing checks the PCB’s performance under real-world conditions to verify that all components function as intended, preventing operational failures.
Q: What is the importance of final inspection in PCBA assembly?
A: Final inspection ensures that the finished PCBA meets all design and functional specifications, ensuring reliability and compliance with quality standards.












