Introduction
In the world of electronics, the right PCB can make or break your design. But with so many options, how do you choose? Let's compare Rig-Flex PCBs and Standard PCBs to help you decide which one is right for your project.
This article will explore the key differences between Rig-Flex and Standard PCBs, their advantages, and how to choose the best one for your needs.
What is a Rig-Flex PCB?
Structure and Material Composition
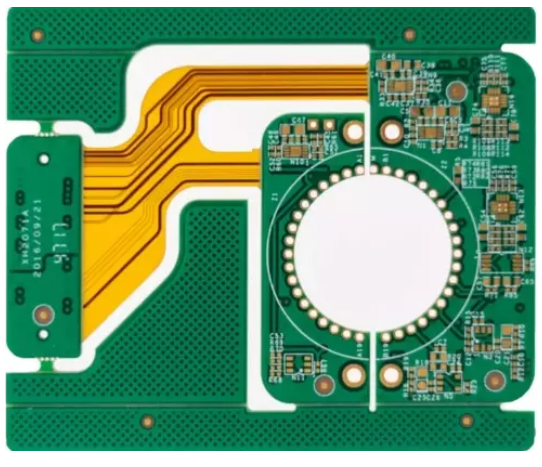
A Rig-Flex PCB is a hybrid printed circuit board that combines both rigid and flexible materials within a single unit. This structure allows it to provide the mechanical support needed in some areas while maintaining the flexibility required in others. The rigid sections are typically made from materials like FR-4, a common and reliable laminate used in rigid PCBs, while the flexible areas are constructed from polyimide or other flexible materials. This unique structure makes Rig-Flex PCBs versatile, enabling them to conform to complex shapes while also offering stability in certain areas.
Key Features of Rig-Flex PCB
The main characteristics of Rig-Flex PCBs include their ability to bend, twist, and fold, which is ideal for applications that require a compact form factor. These boards are also lightweight and can integrate multiple functions into a single, space-efficient design. Their hybrid structure means that Rig-Flex PCBs can combine the best of both worlds, offering both rigidity where needed and flexibility where it’s most beneficial.
Common Uses of Rig-Flex PCBs
Rig-Flex PCBs are commonly used in industries where space-saving and high reliability are paramount. Some of their most notable applications include aerospace, medical devices, automotive electronics, and wearable technology. In these industries, the ability to fit a PCB into compact, dynamic, or irregularly shaped spaces is critical, making Rig-Flex PCBs an ideal choice for such advanced applications.
What is a Standard PCB?
Structure and Material Composition
Standard PCBs, also known as rigid PCBs, are constructed from solid, non-flexible materials like FR-4. The structure of these PCBs is simple and stable, making them ideal for applications where strength and durability are essential. Standard PCBs can be designed with multiple layers, and their materials are typically inexpensive and easy to work with. This simplicity in design and manufacturing has made rigid PCBs the most widely used PCB type in the industry.
Key Features of Standard PCBs
The primary advantage of Standard PCBs lies in their robustness and ability to provide stable mechanical support. These PCBs are ideal for mounting and connecting heavy electronic components, making them suitable for high-performance devices and applications where minimal movement or bending occurs. They are also easier to manufacture, leading to lower production costs and faster turnarounds, especially for mass production.
Common Uses of Standard PCBs
Standard PCBs are used extensively in consumer electronics, such as televisions, smartphones, and computers. They are also commonly found in industrial machinery, power supplies, and large electronic devices where size is less of a concern. Their simplicity and reliability make them the go-to choice for most high-volume manufacturing projects.
Key Differences Between Rig-Flex and Standard PCBs
Flexibility and Form Factor
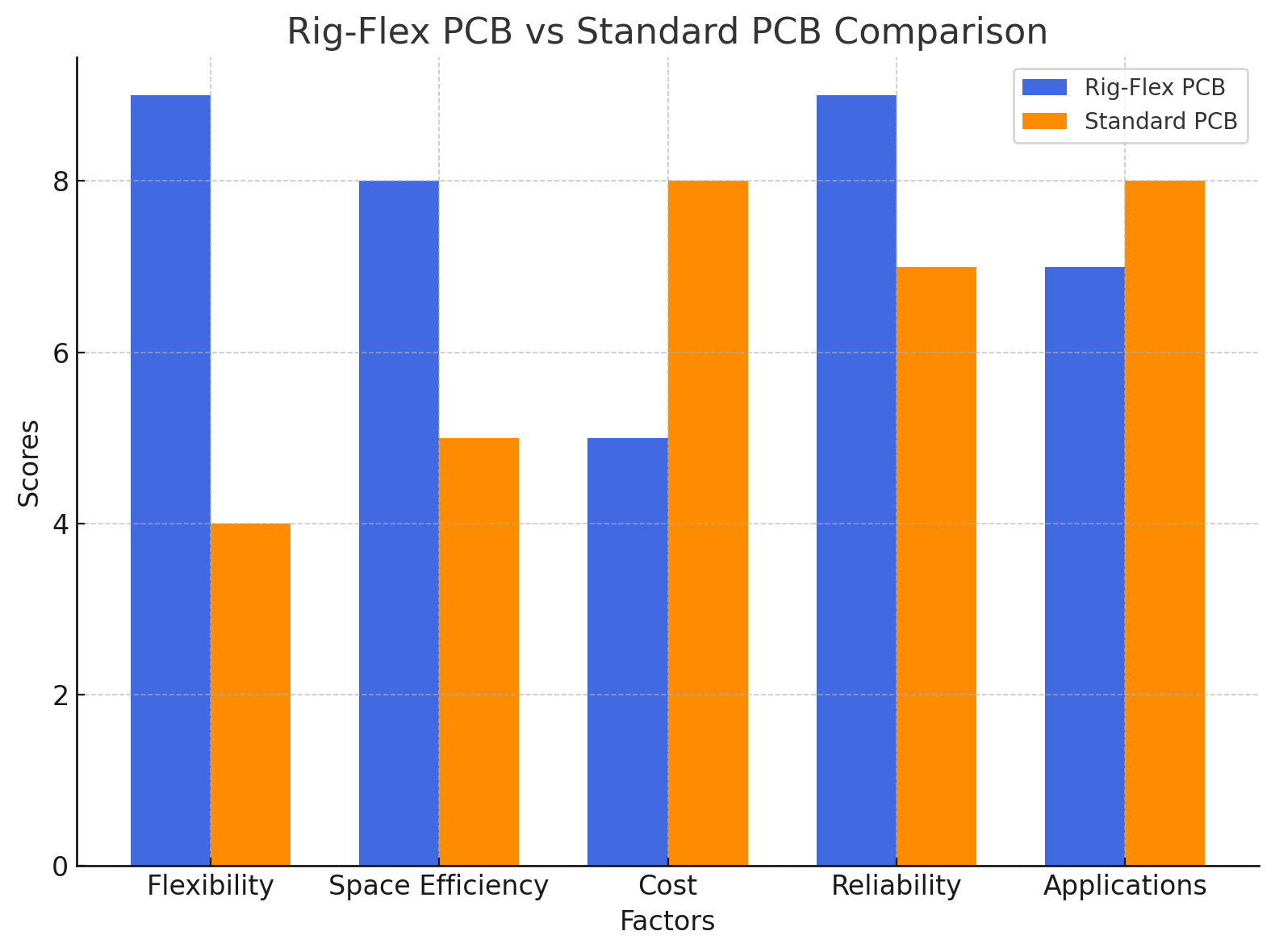
One of the most obvious differences between Rig-Flex and Standard PCBs is flexibility. Standard PCBs are rigid, meaning they cannot bend or conform to specific shapes. This makes them ideal for stable applications where mechanical support is required. On the other hand, Rig-Flex PCBs combine rigid sections with flexible ones, making them capable of bending and adapting to irregular shapes. This flexibility allows for innovative designs and is essential in applications where space is limited or unique shapes are needed.
Space Efficiency and Design Freedom
Rig-Flex PCBs excel in environments where space is a premium. They allow for compact and dynamic designs, integrating rigid and flexible areas in a single unit. This can save valuable space in devices where multiple rigid PCBs and connectors would otherwise be required. Standard PCBs, while providing reliable and stable performance, often require more space due to their rigid nature and are less suited for highly compact applications.
Cost Comparison
Cost is another key differentiator. Standard PCBs are typically cheaper to manufacture due to their simpler design and the widespread availability of materials. Their established manufacturing processes also contribute to lower production costs. Rig-Flex PCBs, however, tend to be more expensive due to their complexity and the need for specialized materials. The extra fabrication steps involved in making the flexible sections and integrating them with rigid parts result in a higher cost per unit.
Attribute | Rig-Flex PCB | Standard PCB |
Structure | Hybrid of rigid and flexible sections | Rigid, made of materials like FR-4 |
Flexibility | Can bend and conform to shapes | Rigid, not flexible |
Space Efficiency | Highly space-saving and compact | Less space-efficient, fixed form |
Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower manufacturing cost |
Application | Wearables, aerospace, medical devices | Consumer electronics, industrial machines |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Rig-Flex PCBs
Advantages of Rig-Flex PCBs
Rig-Flex PCBs offer significant advantages in certain applications. They combine the best of both rigid and flexible PCBs, offering the stability of rigid sections and the flexibility of polyimide materials. This unique design makes them ideal for compact devices where space is limited. Additionally, Rig-Flex PCBs reduce the need for connectors and cables, which simplifies the assembly process, reduces potential failure points, and improves overall reliability.
Disadvantages of Rig-Flex PCBs
However, Rig-Flex PCBs come with some challenges. They are more difficult and expensive to manufacture compared to Standard PCBs. The complexity of the design process, including the handling of multiple materials and the integration of flexible and rigid sections, can lead to higher costs. Additionally, designing for Rig-Flex PCBs requires specialized knowledge and tools, which may make them less accessible for certain projects or teams.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Standard PCBs
Advantages of Standard PCBs
Standard PCBs are cost-effective and straightforward to manufacture. Their reliability and durability make them ideal for high-volume production, particularly for devices where size constraints are not a major concern. The manufacturing process for Standard PCBs is well-established, which allows for efficient production and reduced lead times. This makes them a go-to choice for consumer electronics and industrial applications.
Disadvantages of Standard PCBs
Despite their advantages, Standard PCBs have limitations in terms of flexibility. They are not suited for applications where the PCB needs to bend or fit into irregularly shaped spaces. This lack of flexibility can limit design options in more compact or dynamic products. Additionally, in cases where multiple PCBs need to be interconnected, connectors and cables add bulk and increase the potential for failure.
Application Scenarios: When to Choose Rig-Flex PCB vs Standard PCB
Applications Best Suited for Rig-Flex PCBs
Rig-Flex PCBs are ideal for use in wearable technology, aerospace applications, defense systems, and automotive sensors. These industries require the ability to fit a PCB into tight, dynamic spaces, or endure vibrations and movement. Rig-Flex PCBs provide the flexibility and durability needed in these challenging environments, making them a valuable choice for high-performance systems.
Applications Best Suited for Standard PCBs
Standard PCBs are well-suited for consumer electronics, industrial machinery, and high-power applications. Devices like desktop computers, televisions, and power supplies benefit from the stability and cost-effectiveness that Standard PCBs offer. Their ability to support complex circuits and components in a fixed, stable environment makes them the preferred choice for these applications.
Application Type | Rig-Flex PCB | Standard PCB |
Wearable Devices | Ideal for compact, flexible designs | Not suitable for flexible designs |
Aerospace and Defense | Preferred for high-reliability, dynamic systems | Not commonly used in these sectors |
Medical Devices | Used for compact and reliable devices | Rarely used in medical applications |
Consumer Electronics | Less common due to higher costs | Ideal for mass production and cost-efficiency |
Automotive Sensors | Suitable for complex sensor integration | Standard PCBs used in control systems |
Cost Analysis: Rig-Flex PCBs vs Standard PCBs
Manufacturing Cost
The manufacturing cost of Standard PCBs is generally lower due to the simpler materials and processes involved. In contrast, Rig-Flex PCBs require more complex materials and fabrication steps, which contribute to higher costs. However, the total cost of a Rig-Flex PCB should also factor in the potential savings in system integration, as fewer connectors and cables are needed.
System Integration Cost
Using Rig-Flex PCBs can reduce the need for separate connectors and cables, which can lower overall system integration costs. The compact design and ability to eliminate some components make Rig-Flex PCBs a more efficient choice in certain applications, despite their higher upfront cost.
Cost Factor | Rig-Flex PCB | Standard PCB |
Material Costs | Higher due to flexible material | Lower, primarily FR-4 |
Manufacturing Costs | Higher due to complexity of design | Lower due to simpler design |
Assembly Costs | Lower due to fewer connectors | Higher due to additional connectors |
Total System Cost | Can be higher overall, but reduces complexity | Lower overall cost, but requires more parts |
Conclusion
Choosing between Rig-Flex PCBs and Standard PCBs depends on your project's unique needs. Rig-Flex PCBs are ideal for applications requiring flexibility and space-saving designs, especially in industries like aerospace, medical devices, and wearables. On the other hand, Standard PCBs are better suited for stable, high-volume production where cost and reliability are key.
By evaluating the advantages and application scenarios of both, you can make an informed choice. Whether you need the adaptability of Rig-Flex PCBs or the cost-effective stability of Standard PCBs, understanding the trade-offs will guide your decision. At XDCPCBA, we offer expert PCB solutions to match your specific design requirements.
FAQ
Q: What is the difference between Rig-Flex PCB and Standard PCB?
A: Rig-Flex PCBs combine both rigid and flexible sections, offering flexibility and space-saving benefits. Standard PCBs are rigid and suitable for high-volume, cost-effective applications.
Q: When should I choose a Rig-Flex PCB over a Standard PCB?
A: Choose a Rig-Flex PCB for applications requiring flexibility, compact design, or movement, such as in aerospace, wearables, and medical devices. Standard PCBs are better for stable, high-volume production.
Q: Are Rig-Flex PCBs more expensive than Standard PCBs?
A: Yes, Rig-Flex PCBs are typically more expensive due to their complex manufacturing process, whereas Standard PCBs are more cost-effective for mass production.
Q: Which PCB type is better for space-constrained designs?
A: Rig-Flex PCBs are ideal for space-constrained designs as they offer flexibility to fit into compact, dynamic environments, unlike Standard PCBs, which are rigid and have size limitations.
Q: Can I use Rig-Flex PCBs for high-power applications?
A: Rig-Flex PCBs are not typically used for high-power applications. Standard PCBs, known for their durability and stability, are a better choice for high-power devices.












